Ⅰ Purpose
Simulate the possible microbial contamination (primary pollution and secondary pollution) during the production, storage and consumer use of cosmetics, artificially add quantitative known strains to the product, and regularly track and detect the growth and decline of microorganisms in the product to judge Experiments on the antiseptic effect of preservatives to ensure that the content of microorganisms in cosmetics reaches the standard to the greatest extent.
"Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 Edition)
| Microbiological Indicators |
Limit |
Remarks |
| Total Number of Colonies(CFU/g or CFU/mL) |
≤500 |
Eye Cosmetics, Lip Cosmetics and Children's Cosmetics |
| ≤1000 |
Other Cosmetics |
| Total Number of Molds and Yeasts(CFU/g or CFU/mL) |
≤100 |
- |
| Thermostable Escherichia Coli(g or mL) |
Not Detected |
- |
| Staphylococcus Aaureus (g or mL) |
Not Detected |
- |
| Pseudomonas Aeruginosa (g or mL) |
Not Detected |
- |
Ⅱ Strain Selection
The Same as Microbial Limit Test.
Ⅲ Experimental Method
-
Method 1- One-Time Addition Method
Weigh a certain amount of test sample, add the mixed bacteria suspension in a ratio of 1: x, and require the initial concentration of bacteria in the sample to reach 105*106cfu/g, the initial concentration of yeast and mold to reach 105*106cfu/ g and different concentration gradient bacteriostatic agents. Mix the sample with the bacterial solution thoroughly, seal the mouth of the sample bottle with sealing glue, and store it in an incubator at 25°C. At 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after inoculation, samples were taken to detect the microbial content.
-
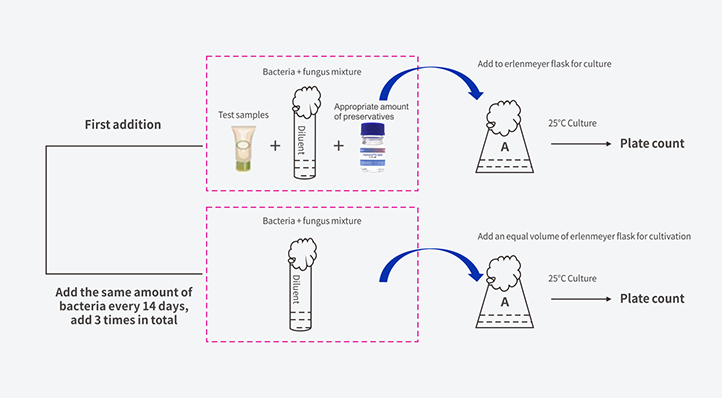
Method 2 - Three-Time Addition Method
Weigh a certain amount of test sample, add the mixed bacteria suspension at a ratio of 1: x, and require the initial concentration of bacteria in the sample to reach 106*107cfu/g, the initial concentration of yeast and mold to reach 105*106cfu/g. After the sample and the bacterial liquid are thoroughly mixed, the mouth of the sample bottle is sealed with a sealing glue and placed in an incubator at 25°C. Next, add the bacteria once every 14 days, and add the bacteria 3 times in total, and the concentration of each addition must meet the requirements. Sampling every seven days after the first addition of bacteria for microbial content testing, that is, sampling and analyzing the bacteria content of the samples on the 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, and 42 days. Among them, the second addition of bacteria was performed after the detection on the 14th day, and the third addition of bacteria after the detection on the 28th day.
Ⅳ Evaluation Standard
CTFA standard
The bacterial species recommended by the the United States Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association (CTFA) are very representative. They have passed the microbiological challenge test according to the CTFA standard and have a 3-year shelf life recognized worldwide.
| Add bacteria for the first time |
Bacterial |
Bacterial:The number of bacteria decreased by more than 99.9% within 7 days, the number of bacteria within 14 days was <10, and it was not detected at 28 days. |
| Molds and Yeasts |
The total number of molds and yeasts was reduced by 90% after 7 days of cultivation, and no longer increased, and passed the test. |
| Add bacteria for the third time |
Excellent antiseptic effect |
That is, after three additions of bacteria, on the 14th day after each addition, the amount of viable bacteria is reduced by 99.9%, which passes the test. |
| The antiseptic effect is acceptable |
After three additions of bacteria, on the 14th day after each addition, the number of viable bacteria is reduced by more than 90%, and the test is passed. |
| Poor antiseptic effect |
That is, after three additions, on the 14th day after each addition, the amount of viable bacteria is reduced by less than 90% of the initial concentration, and the test fails. |
Ⅴ Reference Standard
So far, countries around the world and related organizations have not yet had a unified method for evaluating cosmetic preservative systems, but the basic design is the same. Among them, the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) law and the United States Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association (CTFA) method is two more representative methods.
Our Reference Standard :
United States Pharmacopoeia: USP 39(51)
United States Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association: CTFA
United States Pharmacopoeia: EP 7.0-5.1.3